Climate Tech and Pakistan
November 11, 2022
Is Headless Commerce the future to digital retail ?
December 30, 2022Trade finance has been around for thousands of years. It’s the process of arranging and funding business deals, especially international trade deals. Banks facilitate these transactions by providing letters of credit and performing other financial services on behalf of their clients. However, the current system is slow, cumbersome and costly.
Trade Finance
Trade finance is the process of facilitating the payment of goods and services between two or more parties in an international transaction. It includes all aspects of finance related to trade, including:
- Payment processing by banks or other financial institutions
- Commercial credit insurance against default risk such as war, terrorism and natural disasters. This can be provided by insurers who are often affiliated with banks that offer some form of trade finance service (e.g., Société Générale). These commercial credit insurers may also provide other forms of protection such as guarantees against non-payment for goods ordered from suppliers under contract terms that require prompt performance by customers (see below).
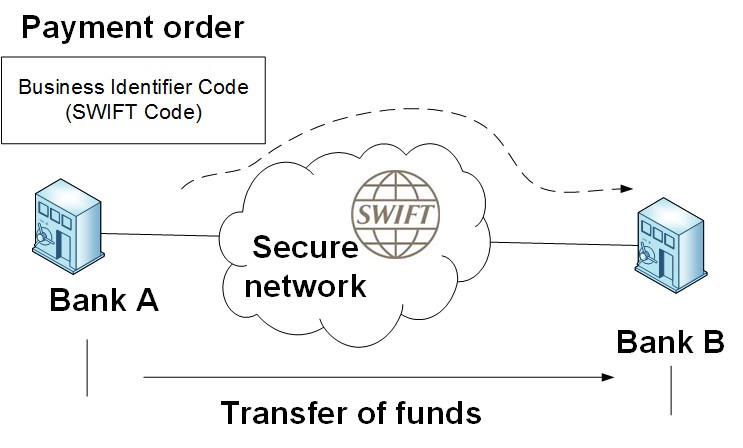
SWIFT – The Slow and Cumbersome Way
The SWIFT network is a messaging system used for international money transfers. It was created in 1973 and is operated by The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT), which has its headquarters in La Hulpe, Belgium.
The SWIFT network consists of three different systems:
- Customer messaging system that allows banks to send messages to each other about payments and other financial transactions;
- Core Network that connects these customer messaging systems together;
- Integrator Directory Service (IDS), which connects the core network with the internal infrastructure of each institution using it.
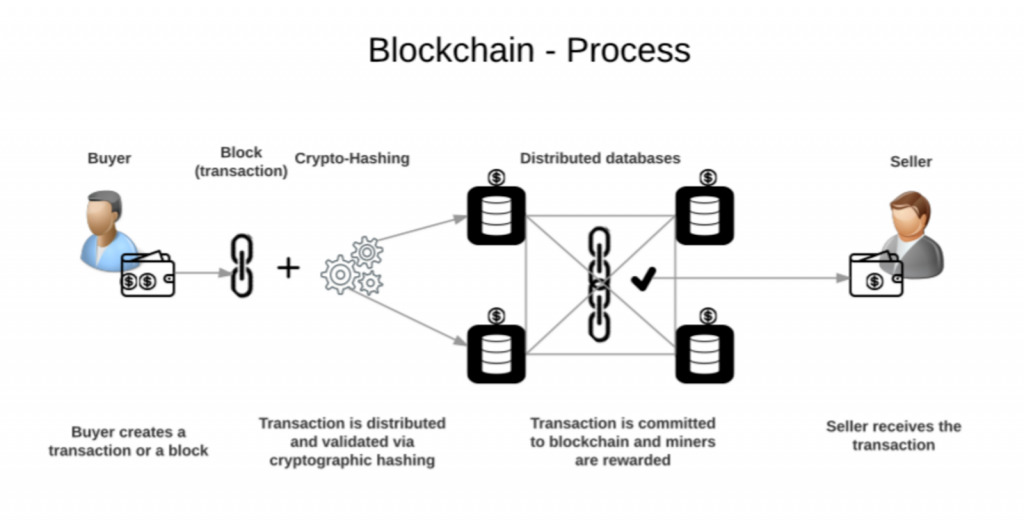
Payments on DLT/Blockchain – The Web 3.0 Way – Instantaneous, Permissioned, Transparent and Immutable
The payments on blockchain are instant, permissioned and transparent. They are immutable (can’t be changed) and an open ledger that anyone can access. These features make it possible for you to see exactly how much money is in your account at all times, which means you don’t have to rely on someone else’s word about what happened when they said something happened.
It’s also important to note that blockchains aren’t just about storing data; they’re actually distributed ledgers: there are multiple copies of the same information across different computers on a network so even if one copy gets corrupted or hacked another copy will still be available – which makes them extremely secure!
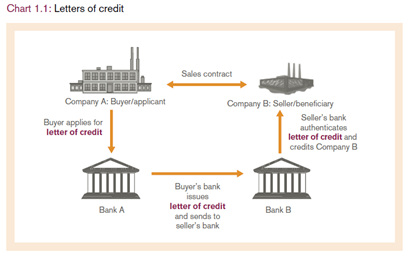
Letters of Credit, Bills of Collections and the Blockchain
Letters of Credit (LCs) are a common way to secure payment in international trade. Bills of Collections are another way to secure payment in international trade. The blockchain can be used to automate the issuance and settlement of LCs and Bills of Collections.
Letters Of Credit : A Letter Of Credit is an instrument issued by one bank against another bank, which allows the first bank that issues it, or its agent(s), to draw on a drawer’s account at his/her own discretion without requiring any prior approval or notice from him/herself or his clients; this may be done for various reasons including but not limited to:
- To finance purchases by customers abroad through banks located in different countries;
- To facilitate payments between two parties who don’t know each other yet want them done quickly because they need money urgently;
- For obtaining funds on behalf of clients without having them directly involved in such transactions themselves
Bid on Letters of Credit
Bid on Letters of Credit, Bills of Collections and the Blockchain
The Web 3.0 Way
The Bid on Letter of Credit (BLOC) is a payment method that allows you to pay for goods or services using blockchain technology. It’s similar to a bank wire transfer but with one notable difference: instead of sending your funds directly from your bank account over the internet, they are held in escrow until they’re released by their recipient. This means that there’s no intermediary involved between buyer and seller—you don’t have to trust anyone else but yourself when it comes time for payment!
New solutions for trade finance are needed to increase liquidity and reduce counterparty risk.
- New solutions are needed to increase liquidity and reduce counterparty risk.
- Blockchain can help with payments on the blockchain, and letters of credit on the blockchain.
Conclusion
Trade finance is a long-standing problem. It’s time to bring it into the 21st century and make it faster, less expensive and more secure.